- Javascript
- Python
AI SDK
Cloudflare Agents
LangGraph
GenKit
LlamaIndex
NextJS-Auth0
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:npm install @auth0/ai-vercel
import { Auth0AI } from "@auth0/ai-vercel";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
const auth0AI = new Auth0AI();
export const withGoogleCalendar = auth0AI.withTokenVault({
connection: "google-oauth2",
scopes: ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"],
refreshToken: async () => {
const session = await auth0.getSession();
const refreshToken = session?.tokenSet.refreshToken as string;
return refreshToken;
},
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation.
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.import { addHours, formatISO } from "date-fns";
import { GaxiosError } from "gaxios";
import { google } from "googleapis";
import { getAccessTokenFromTokenVault } from "@auth0/ai-vercel";
import { TokenVaultError } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { withGoogleCalendar } from "@/lib/auth0-ai";
import { tool } from "ai";
import { z } from "zod";
export const checkUsersCalendar = withGoogleCalendar(
tool({
description:
"Check user availability on a given date time on their calendar",
parameters: z.object({
date: z.coerce.date(),
}),
execute: async ({ date }) => {
// Get the access token from Auth0 AI
const accessToken = getAccessTokenFromTokenVault();
// Google SDK
try {
const calendar = google.calendar("v3");
const auth = new google.auth.OAuth2();
auth.setCredentials({
access_token: accessToken,
});
const response = await calendar.freebusy.query({
auth,
requestBody: {
timeMin: formatISO(date),
timeMax: addHours(date, 1).toISOString(),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
},
});
return {
available: response.data?.calendars?.primary?.busy?.length === 0,
};
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof GaxiosError) {
if (error.status === 401) {
throw new TokenVaultError(
`Authorization required to access the Token Vault connection`
);
}
}
throw error;
}
},
})
);
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action—such as authenticating or granting API access—before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages authentication redirects in the Vercel AI SDK via these interrupts.Server Side
On the server-side code of your Next.js App, you need to set up the tool invocation and handle the interruption messaging via theerrorSerializer. The setAIContext function is used to set the async-context for the Auth0 AI SDK.import { createDataStreamResponse, Message, streamText } from "ai";
import { checkUsersCalendar } from "@/lib/tools/";
import { setAIContext } from "@auth0/ai-vercel";
import { errorSerializer, withInterruptions } from "@auth0/ai-vercel/interrupts";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const { id, messages} = await request.json();
const tools = { checkUsersCalendar };
setAIContext({ threadID: id });
return createDataStreamResponse({
execute: withInterruptions(
async (dataStream) => {
const result = streamText({
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
system: "You are a friendly assistant! Keep your responses concise and helpful.",
messages,
maxSteps: 5,
tools,
});
result.mergeIntoDataStream(dataStream, {
sendReasoning: true,
});
},
{ messages, tools }
),
onError: errorSerializer((err) => {
console.log(err);
return "Oops, an error occured!";
}),
});
}
Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with Google Calendar and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
"use client";
import { useChat } from "@ai-sdk/react";
import { useInterruptions } from "@auth0/ai-vercel/react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
export default function Chat() {
const { messages, handleSubmit, input, setInput, toolInterrupt } =
useInterruptions((handler) =>
useChat({
onError: handler((error) => console.error("Chat error:", error)),
})
);
return (
<div>
{messages.map((message) => (
<div key={message.id}>
{message.role === "user" ? "User: " : "AI: "}
{message.content}
</div>
))}
{TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(toolInterrupt) && (
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
interrupt={toolInterrupt}
connectWidget={{
title: "Check your availability in Google Calendar",
description:"description ...",
action: { label: "Check" },
}}
/>
)}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input value={input} placeholder="Say something..." onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)} />
</form>
</div>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
- Auth0 Hono Web SDK: for the Worker.
- Auth0 Cloudflare Agents API SDK for the Chat Agent.
npm install @auth0/ai-vercel @auth0/ai-cloudflare @auth0/ai
import { Auth0AI, setGlobalAIContext } from "@auth0/ai-vercel";
import { getCurrentAgent } from "agents";
import type { Chat } from "./chat";
const getAgent = () => {
const { agent } = getCurrentAgent<Chat>();
if (!agent) {
throw new Error("No agent found");
}
return agent;
};
setGlobalAIContext(() => ({ threadID: getAgent().name }));
const auth0AI = new Auth0AI({
store: () => {
return getAgent().auth0AIStore;
},
});
const refreshToken = async () => {
const credentials = getAgent().getCredentials();
return credentials?.refresh_token;
};
export const withGoogleCalendar = auth0AI.withTokenVault({
refreshToken,
connection: "google-oauth2",
scopes: ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"],
});
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.import { getAccessTokenFromTokenVault } from "@auth0/ai-vercel";
import { TokenVaultError } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { tool } from "ai";
import { addHours } from "date-fns";
import { z } from "zod";
import { withGoogleCalendar } from "../auth0-ai";
export const checkUsersCalendar = withGoogleCalendar(
tool({
description:
"Check user availability on a given date time on their calendar",
inputSchema: z.object({
date: z.coerce.date(),
}),
execute: async ({ date }) => {
// Get the access token from Auth0 AI
const accessToken = getAccessTokenFromTokenVault();
const url = "https://www.googleapis.com/calendar/v3/freeBusy";
const body = JSON.stringify({
timeMin: date,
timeMax: addHours(date, 1),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
});
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body,
});
if (!response.ok) {
if (response.status === 401) {
throw new TokenVaultError(
"Authorization required to access the Federated Connection"
);
}
throw new Error(
`Invalid response from Google Calendar API: ${
response.status
} - ${await response.text()}`
);
}
const busyResp = await response.json();
return { available: busyResp.calendars.primary.busy.length === 0 };
},
})
);
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action—such as authenticating or granting API access—before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages authentication redirects in the Vercel AI SDK via these interrupts.Server Side
On the Chat agent class, you need to set up the tool invocation and handle the interruption messaging via theerrorSerializer.import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
import { CloudflareKVStore } from "@auth0/ai-cloudflare";
import {
errorSerializer,
invokeTools,
withInterruptions,
} from "@auth0/ai-vercel/interrupts";
import { AIChatAgent } from "agents/ai-chat-agent";
import {
convertToModelMessages,
createUIMessageStream,
createUIMessageStreamResponse,
generateId,
stepCountIs,
streamText,
type UIMessage,
} from "ai";
import { extend } from "flumix";
import { executions, tools } from "./tools";
import { processToolCalls } from "./utils";
import { AsyncUserConfirmationResumer } from "@auth0/ai-cloudflare";
import { AuthAgent, OwnedAgent } from "@auth0/auth0-cloudflare-agents-api";
const model = openai("gpt-4o-2024-11-20");
const SuperAgent = extend(AIChatAgent<Env>)
.with(AuthAgent)
.with(OwnedAgent)
.with(AsyncUserConfirmationResumer)
.build();
export class Chat extends SuperAgent {
messages: UIMessage[] = [];
async onChatMessage() {
const allTools = {
...tools,
...(this.mcp?.getAITools?.() ?? {}),
};
const claims = this.getClaims?.();
const stream = createUIMessageStream({
originalMessages: this.messages,
execute: withInterruptions(
async ({ writer }) => {
await invokeTools({
messages: await convertToModelMessages(this.messages),
tools: allTools,
});
const processed = await processToolCalls({
messages: this.messages,
dataStream: writer,
tools: allTools,
executions,
});
const result = streamText({
model,
stopWhen: stepCountIs(10),
messages: await convertToModelMessages(processed),
system: `You are a helpful assistant that can do various tasks...
If the user asks to schedule a task, use the schedule tool to schedule the task.
The name of the user is ${claims?.name ?? "unknown"}.`,
tools: allTools,
onStepFinish: (output) => {
if (output.finishReason === "tool-calls") {
const last = output.content[output.content.length - 1];
if (last?.type === "tool-error") {
const { toolName, toolCallId, error, input } = last;
const serializableError = {
cause: error,
toolCallId,
toolName,
toolArgs: input,
};
throw serializableError;
}
}
},
});
writer.merge(
result.toUIMessageStream({
sendReasoning: true,
})
);
},
{ messages: this.messages, tools: allTools }
),
onError: errorSerializer(),
});
return createUIMessageStreamResponse({ stream });
}
async executeTask(description: string) {
await this.saveMessages([
...this.messages,
{
id: generateId(),
role: "user",
parts: [
{ type: "text", text: `Running scheduled task: ${description}` },
],
},
]);
}
get auth0AIStore() {
return new CloudflareKVStore({ kv: this.env.Session });
}
}
CloudflareKVStore instance with your Cloudflare agent worker, you can use Workers KV and a KV namespace as the persistent store. This enables you to store Auth0 session data and other key-value pairs with easy access from your Cloudflare agent workers.import { CloudflareKVStore } from '@auth0/ai-cloudflare';
...
return new CloudflareKVStore({ kv: this.env.YOUR_KV_NAMESPACE });
kv prop accepts any store which implements the KVNamespace interface, so any persistent store which implements this interface will work.Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with Google Calendar and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
"use client";
import { useChat } from "@ai-sdk/react";
import { useAgentChatInterruptions } from "@auth0/ai-cloudflare/react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
export default function Chat() {
const agent = useAgent({
agent: "chat",
name: threadID ?? undefined,
});
const chat = useAgentChatInterruptions({
agent,
id: threadID,
});
const {
messages: agentMessages,
sendMessage: handleAgentSubmit,
addToolResult,
clearHistory,
toolInterrupt,
} = chat;
return (
<Layout>
{agentMessages.map((m: UIMessage, index) => {
const isUser = m.role === "user";
return (
<div key={`${m.id}-${index}`}>
{showDebug && (
<pre className="text-xs text-muted-foreground overflow-scroll">
{JSON.stringify(m, null, 2)}
</pre>
)}
<div className={`flex ${isUser ? "justify-end" : "justify-start"}`}>
<div
className={`flex gap-2 max-w-[85%] ${
isUser ? "flex-row-reverse" : "flex-row"
}`}
>
<div>
<div>
{m.parts?.map((part: any, i) => {
if (
part?.type?.startsWith("tool-") &&
toolInterrupt &&
TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(toolInterrupt)
) {
return (
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
key={toolInterrupt?.toolCall?.id}
interrupt={toolInterrupt}
auth={{ authorizePath: "/auth/login" }}
connectWidget={{
icon: (
<div className="bg-gray-200 p-3 rounded-lg flex-wrap">
<GoogleCalendarIcon />
</div>
),
title: "Google Calendar Access",
description:
"We need access to your google Calendar in order to call this tool...",
action: { label: "Grant" },
}}
/>
);
}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
})}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
value={input}
placeholder="Say something..."
onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)}
/>
</form>
</Layout>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
Create a Custom API Client in Auth0
- Navigate to Applications > APIs
- Click the Create API button to create a new Custom API.
- Go to the Custom API you created and click the Add Application button in the right top corner.
- Once you've added the API as an application, click the Configure Application button in the right top corner.
- Note down the
client idandclient secretfor your environment variables.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:npm install @auth0/ai-langchain
import { SUBJECT_TOKEN_TYPES } from "@auth0/ai";
import { Auth0AI } from "@auth0/ai-langchain";
const auth0AI = new Auth0AI({
auth0: {
domain: process.env.AUTH0_DOMAIN!,
clientId: process.env.AUTH0_CUSTOM_API_CLIENT_ID!,
clientSecret: process.env.AUTH0_CUSTOM_API_CLIENT_SECRET!,
},
});
const withAccessTokenForConnection = (connection: string, scopes: string[]) =>
auth0AI.withTokenVault({
connection,
scopes,
accessToken: async (_, config) => {
return config.configurable?.langgraph_auth_user?.getRawAccessToken();
},
subjectTokenType: SUBJECT_TOKEN_TYPES.SUBJECT_TYPE_ACCESS_TOKEN,
});
export const withGoogleCalendar = withAccessTokenForConnection(
"google-oauth2",
["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"]
);
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.import { addHours, formatISO } from "date-fns";
import { GaxiosError } from "gaxios";
import { google } from "googleapis";
import { getAccessTokenFromTokenVault } from "@auth0/ai-langchain";
import { TokenVaultError } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { withGoogleCalendar } from "@/lib/auth0-ai";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
export const checkUsersCalendar = withGoogleCalendar(
tool(async ({ date }) => {
// Get the access token from Auth0 AI
const accessToken = getAccessTokenFromTokenVault();
// Google SDK
try {
const calendar = google.calendar("v3");
const auth = new google.auth.OAuth2();
auth.setCredentials({
access_token: accessToken,
});
const response = await calendar.freebusy.query({
auth,
requestBody: {
timeMin: formatISO(date),
timeMax: addHours(date, 1).toISOString(),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
},
});
return {
available: response.data?.calendars?.primary?.busy?.length === 0,
};
} catch (err) {
if (err instanceof GaxiosError && err.status === 401) {
throw new TokenVaultError(
`Authorization required to access the Token Vault connection`
);
}
throw err;
}
},
{
name: "check_user_calendar",
description:
"Use this function to check if the user is available on a certain date and time",
schema: z.object({
date: z.coerce.date(),
}),
})
);
ToolNode. The agent will automatically request the access token when the tool is called.import { AIMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
import { RunnableLike } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
import { END, InMemoryStore, MemorySaver, MessagesAnnotation, START, StateGraph } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { checkUsersCalendar } from "@/lib/tools/checkUsersCalendar";
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-4o", }).bindTools([
checkUsersCalendar,
]);
const callLLM = async (state: typeof MessagesAnnotation.State) => {
const response = await model.invoke(state.messages);
return { messages: [response] };
};
const routeAfterLLM: RunnableLike = function (state) {
const lastMessage = state.messages[state.messages.length - 1] as AIMessage;
if (!lastMessage.tool_calls?.length) {
return END;
}
return "tools";
};
const stateGraph = new StateGraph(MessagesAnnotation)
.addNode("callLLM", callLLM)
.addNode(
"tools",
new ToolNode(
[
// A tool with Token Vault access
checkUsersCalendar,
// ... other tools
],
{
// Error handler should be disabled in order to
// trigger interruptions from within tools.
handleToolErrors: false,
}
)
)
.addEdge(START, "callLLM")
.addConditionalEdges("callLLM", routeAfterLLM, [END, "tools"])
.addEdge("tools", "callLLM");
const checkpointer = new MemorySaver();
const store = new InMemoryStore();
export const graph = stateGraph.compile({
checkpointer,
store,
interruptBefore: [],
interruptAfter: [],
});
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action —such as authenticating or granting API access— before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages such authentication redirects integrated with the Langchain SDK.Server Side
On the server side of your Next.js application you need to set up a route to handle the Chat API requests. This route will be responsible for forwarding the requests to the LangGraph API. Additionally, you must provide theaccessToken in the headers.import { initApiPassthrough } from "langgraph-nextjs-api-passthrough";
import { NextRequest } from "next/server";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
async function getAccessToken() {
const tokenResult = await auth0.getAccessToken();
if (!tokenResult?.token) {
throw new Error("Error retrieving access token for langgraph api.");
}
return tokenResult.token;
}
export const { GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, runtime } =
initApiPassthrough({
apiUrl: process.env.LANGGRAPH_API_URL,
apiKey: process.env.LANGSMITH_API_KEY,
runtime: "edge",
baseRoute: "langgraph/",
headers: async (req: NextRequest) => {
const headers: Record<string, string> = {};
req.headers.forEach((value, key) => {
headers[key] = value;
});
const accessToken = await getAccessToken();
headers["Authorization"] = `Bearer ${accessToken}`;
return headers;
},
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation. :::
Add Custom Authentication
{
"node_version": "20",
"graphs": {
"agent": "./src/lib/agent.ts:agent"
},
"env": ".env",
"auth": {
"path": "./src/lib/auth.ts:authHandler"
}
}
import { createRemoteJWKSet, jwtVerify } from "jose";
const { Auth, HTTPException } = require("@langchain/langgraph-sdk/auth");
const AUTH0_DOMAIN = process.env.AUTH0_DOMAIN;
const AUTH0_AUDIENCE = process.env.AUTH0_AUDIENCE;
// JWKS endpoint for Auth0
const JWKS = createRemoteJWKSet(
new URL(`https://${AUTH0_DOMAIN}/.well-known/jwks.json`)
);
// Create the Auth instance
const auth = new Auth();
// Register the authentication handler
auth.authenticate(async (request: Request) => {
const authHeader = request.headers.get("Authorization");
const xApiKeyHeader = request.headers.get("x-api-key");
/**
* LangGraph Platform will convert the `Authorization` header from the client to an `x-api-key` header automatically
* as of now: https://docs.langchain.com/langgraph-platform/custom-auth
*
* We can still leverage the `Authorization` header when served in other infrastructure w/ langgraph-cli
* or when running locally.
*/
// This header is required in Langgraph Cloud.
if (!authHeader && !xApiKeyHeader) {
throw new HTTPException(401, {
message: "Invalid auth header provided.",
});
}
// prefer the xApiKeyHeader first
let token = xApiKeyHeader || authHeader;
// Remove "Bearer " prefix if present
if (token && token.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
token = token.substring(7);
}
// Validate Auth0 Access Token using common JWKS endpoint
if (!token) {
throw new HTTPException(401, {
message:
"Authorization header format must be of the form: Bearer <token>",
});
}
if (token) {
try {
// Verify the JWT using Auth0 JWKS
const { payload } = await jwtVerify(token, JWKS, {
issuer: `https://${AUTH0_DOMAIN}/`,
audience: AUTH0_AUDIENCE,
});
console.log("✅ Auth0 JWT payload resolved!", payload);
// Return the verified payload - this becomes available in graph nodes
return {
identity: payload.sub!,
email: payload.email as string,
permissions:
typeof payload.scope === "string" ? payload.scope.split(" ") : [],
auth_type: "auth0",
// include the access token for use with Auth0 Token Vault exchanges by tools
getRawAccessToken: () => token,
// Add any other claims you need
...payload,
};
} catch (jwtError) {
console.log(
"Auth0 JWT validation failed:",
jwtError instanceof Error ? jwtError.message : "Unknown error"
);
throw new HTTPException(401, {
message: "Invalid Authorization token provided.",
});
}
}
});
export { auth as authHandler };
Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with Google Calendar and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
import { useStream } from "@langchain/langgraph-sdk/react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
const useFocus = () => {
const htmlElRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
const setFocus = () => {
if (!htmlElRef.current) {
return;
}
htmlElRef.current.focus();
};
return [htmlElRef, setFocus] as const;
};
export default function Chat() {
const [threadId, setThreadId] = useQueryState("threadId");
const [input, setInput] = useState("");
const thread = useStream({
apiUrl: `${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_URL}/api/langgraph`,
assistantId: "agent",
threadId,
onThreadId: setThreadId,
onError: (err) => {
console.dir(err);
},
});
const [inputRef, setInputFocus] = useFocus();
useEffect(() => {
if (thread.isLoading) {
return;
}
setInputFocus();
}, [thread.isLoading, setInputFocus]);
const handleSubmit: FormEventHandler<HTMLFormElement> = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
thread.submit(
{ messages: [{ type: "human", content: input }] },
{
optimisticValues: (prev) => ({
messages: [
...((prev?.messages as []) ?? []),
{ type: "human", content: input, id: "temp" },
],
}),
}
);
setInput("");
};
return (
<div>
{thread.messages.filter((m) => m.content && ["human", "ai"].includes(m.type)).map((message) => (
<div key={message.id}>
{message.type === "human" ? "User: " : "AI: "}
{message.content as string}
</div>
))}
{thread.interrupt && TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(thread.interrupt.value) ? (
<div key={thread.interrupt.ns?.join("")}>
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
interrupt={thread.interrupt.value}
onFinish={() => thread.submit(null)}
connectWidget={{
title: "Check your availability in Google Calendar",
description:"description ...",
action: { label: "Check" },
}}
/>
</div>
) : null}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input ref={inputRef} value={input} placeholder="Say something..." readOnly={thread.isLoading} disabled={thread.isLoading} onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)} />
</form>
</div>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:npm install @auth0/ai-genkit
import { Auth0AI } from "@auth0/ai-genkit";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
// importing GenKit instance
import { ai } from "./genkit";
const auth0AI = new Auth0AI({
genkit: ai,
});
export const withGoogleCalendar = auth0AI.withTokenVault({
connection: "google-oauth2",
scopes: ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"],
refreshToken: async () => {
const session = await auth0.getSession();
const refreshToken = session?.tokenSet.refreshToken as string;
return refreshToken;
},
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation.
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.import { addHours } from "date-fns";
import { z } from "zod";
import { getAccessTokenFromTokenVault } from "@auth0/ai-genkit";
import { TokenVaultError } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { withGoogleCalendar } from "@/lib/auth0-ai";
// importing GenKit instance
import { ai } from "../genkit";
export const checkUsersCalendar = ai.defineTool(
...withGoogleCalendar(
{
description:
"Check user availability on a given date time on their calendar",
inputSchema: z.object({
date: z.coerce
.date()
.describe("Date to check availability for in UTC time always."),
}),
name: "checkUsersCalendar",
},
async ({ date }) => {
// Get the access token from Auth0 AI
const accessToken = getAccessTokenFromTokenVault();
// Google SDK
try {
const calendar = google.calendar("v3");
const auth = new google.auth.OAuth2();
auth.setCredentials({
access_token: .accessToken,
});
const response = await calendar.freebusy.query({
auth,
requestBody: {
timeMin: formatISO(date),
timeMax: addHours(date, 1).toISOString(),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
},
});
return {
available: response.data?.calendars?.primary?.busy?.length === 0,
};
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof GaxiosError) {
if (error.status === 401) {
throw new TokenVaultError(
`Authorization required to access the Token Vault connection`
);
}
}
throw error;
}
}
)
);
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action—such as authenticating or granting API access—before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages authentication redirects in the GenKit SDK via these interrupts.Server Side
On the server-side code of your Next.js App, you need to set up the tool invocation and handle the interruption messaging via theerrorSerializer. The setAIContext function is used to set the async-context for the Auth0 AI SDK.import { ToolRequestPart } from "genkit";
import path from "path";
import { ai } from "@/lib/genkit";
import { checkUsersCalendar } from "@/lib/tools/check-user-calendar";
import { resumeAuth0Interrupts } from "@auth0/ai-genkit";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
export async function POST(
request: Request,
{ params }: { params: Promise<{ id: string }> }
) {
const auth0Session = await auth0.getSession();
const { id } = await params;
const {
message,
interruptedToolRequest,
timezone,
}: {
message?: string;
interruptedToolRequest?: ToolRequestPart;
timezone: { region: string; offset: number };
} = await request.json();
let session = await ai.loadSession(id);
if (!session) {
session = ai.createSession({
sessionId: id,
});
}
const tools = [checkUsersCalendar];
const chat = session.chat({
tools: tools,
system: `You are a helpful assistant.
The user's timezone is ${timezone.region} with an offset of ${timezone.offset} minutes.
User's details: ${JSON.stringify(auth0Session?.user, null, 2)}.
You can use the tools provided to help the user.
You can also ask the user for more information if needed.
Chat started at ${new Date().toISOString()}
`,
});
const r = await chat.send({
prompt: message,
resume: resumeAuth0Interrupts(tools, interruptedToolRequest),
});
return Response.json({ messages: r.messages, interrupts: r.interrupts });
}
export async function GET(
request: Request,
{ params }: { params: Promise<{ id: string }> }
) {
const { id } = await params;
const session = await ai.loadSession(id);
if (!session) {
return new Response("Session not found", {
status: 404,
});
}
const json = session.toJSON();
if (!json?.threads?.main) {
return new Response("Session not found", {
status: 404,
});
}
return Response.json(json.threads.main);
}
Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with Google Calendar and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
"use client";
import { useQueryState } from "nuqs";
import { FormEventHandler, useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
import Markdown from "react-markdown";
const useFocus = () => {
const htmlElRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
const setFocus = () => {
if (!htmlElRef.current) {
return;
}
htmlElRef.current.focus();
};
return [htmlElRef, setFocus] as const;
};
export default function Chat() {
const [threadId, setThreadId] = useQueryState("threadId");
const [input, setInput] = useState("");
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<
{
role: "user" | "model";
content: [{ text?: string; metadata?: { interrupt?: any } }];
}[]
>([]);
useEffect(() => {
if (!threadId) {
setThreadId(self.crypto.randomUUID());
}
}, [threadId, setThreadId]);
useEffect(() => {
if (!threadId) {
return;
}
setIsLoading(true);
(async () => {
const messagesResponse = await fetch(`/api/chat/${threadId}`, {
method: "GET",
credentials: "include",
});
if (!messagesResponse.ok) {
setMessages([]);
} else {
setMessages(await messagesResponse.json());
}
setIsLoading(false);
})();
}, [threadId]);
const [inputRef, setInputFocus] = useFocus();
useEffect(() => {
if (isLoading) {
return;
}
setInputFocus();
}, [isLoading, setInputFocus]);
const submit = async ({
message,
interruptedToolRequest,
}: {
message?: string;
interruptedToolRequest?: any;
}) => {
setIsLoading(true);
const timezone = {
region: Intl.DateTimeFormat().resolvedOptions().timeZone,
offset: new Date().getTimezoneOffset(),
};
const response = await fetch(`/api/chat/${threadId}`, {
method: "POST",
credentials: "include",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({ message, interruptedToolRequest, timezone }),
});
if (!response.ok) {
console.error("Error sending message");
} else {
const { messages: messagesResponse } = await response.json();
setMessages(messagesResponse);
}
setIsLoading(false);
};
// //When the user submits a message, add it to the list of messages and resume the conversation.
const handleSubmit: FormEventHandler<HTMLFormElement> = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
setMessages((messages) => [
...messages,
{ role: "user", content: [{ text: input }] },
]);
submit({ message: input });
setInput("");
};
return (
<div>
{messages
.filter(
(m) =>
["model", "user", "tool"].includes(m.role) &&
m.content?.length > 0 &&
(m.content[0].text || m.content[0].metadata?.interrupt)
)
.map((message, index) => (
<div key={index}>
<Markdown>
{(message.role === "user" ? "User: " : "AI: ") +
(message.content[0].text || "")}
</Markdown>
{!isLoading &&
message.content[0].metadata?.interrupt &&
TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(
message.content[0].metadata?.interrupt
)
? (() => {
const interrupt: any = message.content[0].metadata?.interrupt;
return (
<div>
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
onFinish={() => submit({ interruptedToolRequest: message.content[0] })}
interrupt={interrupt}
connectWidget={{
title: `Requested by: "${interrupt.toolCall.toolName}"`,
description: "Description...",
action: { label: "Check" },
}}
/>
</div>
);
})()
: null}
</div>
))}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input value={input} ref={inputRef} placeholder="Say something..." readOnly={isLoading} disabled={isLoading} onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)} />
</form>
</div>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:npm install @auth0/ai-llamaindex
import { Auth0AI } from "@auth0/ai-llamaindex";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
const auth0AI = new Auth0AI();
export const withGoogleCalendar = auth0AI.withTokenVault({
connection: "google-oauth2",
scopes: ["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"],
refreshToken: async () => {
const session = await auth0.getSession();
const refreshToken = session?.tokenSet.refreshToken as string;
return refreshToken;
},
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation.
2. Integrate your tool with GitHub
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the GitHub API.import { addHours, formatISO } from "date-fns";
import { GaxiosError } from "gaxios";
import { google } from "googleapis";
import { tool } from "llamaindex";
import { withGoogleCalendar } from "@/lib/auth0-ai";
import { getAccessTokenFromTokenVault } from "@auth0/ai-llamaindex";
import { TokenVaultError } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { z } from "zod";
export const checkUsersCalendar = () =>
withGoogleCalendar(
tool(
async ({ date }) => {
// Get the access token from Auth0 AI
const accessToken = getAccessTokenFromTokenVault();
// Google SDK
try {
const calendar = google.calendar("v3");
const auth = new google.auth.OAuth2();
auth.setCredentials({
access_token: accessToken,
});
const response = await calendar.freebusy.query({
auth,
requestBody: {
timeMin: formatISO(date),
timeMax: addHours(date, 1).toISOString(),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
},
});
return {
available: response.data?.calendars?.primary?.busy?.length === 0,
};
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof GaxiosError) {
if (error.status === 401) {
throw new TokenVaultError(
`Authorization required to access the Token Vault connection`
);
}
}
throw error;
}
},
{
name: "checkUsersCalendar",
description:
"Check user availability on a given date time on their calendar",
parameters: z.object({
date: z.coerce.date(),
}),
}
)
);
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action —such as authenticating or granting API access— before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages authentication redirects in the LlamaIndex SDK via these interrupts.Server Side
On the server-side code of your Next.js App, you need to set up the tool invocation and handle the interruption messaging via theerrorSerializer. The setAIContext function is used to set the async-context for the Auth0 AI SDK.import { createDataStreamResponse, LlamaIndexAdapter, Message, ToolExecutionError } from "ai";
import { listRepositories } from "@/lib/tools/";
import { setAIContext } from "@auth0/ai-llamaindex";
import { withInterruptions } from "@auth0/ai-llamaindex/interrupts";
import { errorSerializer } from "@auth0/ai-vercel/interrupts";
import { OpenAIAgent } from "llamaindex";
export async function POST(request: Request) {
const { id, messages }: { id: string; messages: Message[] } =
await request.json();
setAIContext({ threadID: id });
return createDataStreamResponse({
execute: withInterruptions(
async (dataStream) => {
const agent = new OpenAIAgent({
systemPrompt: "You are an AI assistant",
tools: [listRepositories()],
verbose: true,
});
const stream = await agent.chat({
message: messages[messages.length - 1].content,
stream: true,
});
LlamaIndexAdapter.mergeIntoDataStream(stream as any, { dataStream });
},
{
messages,
errorType: ToolExecutionError,
}
),
onError: errorSerializer((err) => {
console.log(err);
return "Oops, an error occured!";
}),
});
}
Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with GitHub and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
"use client";
import { generateId } from "ai";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
import { useInterruptions } from "@auth0/ai-vercel/react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { useChat } from "@ai-sdk/react";
export default function Chat() {
const { messages, handleSubmit, input, setInput, toolInterrupt } =
useInterruptions((handler) =>
useChat({
experimental_throttle: 100,
sendExtraMessageFields: true,
generateId,
onError: handler((error) => console.error("Chat error:", error)),
})
);
return (
<div>
{messages.map((message) => (
<div key={message.id}>
{message.role === "user" ? "User: " : "AI: "}
{message.content}
{message.parts && message.parts.length > 0 && (
<div>
{toolInterrupt?.toolCall.id.includes(message.id) &&
TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(toolInterrupt) && (
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
interrupt={toolInterrupt}
connectWidget={{
title: `Requested by: "${toolInterrupt.toolCall.name}"`,
description: "Description...",
action: { label: "Check" },
}}
/>
)}
</div>
)}
</div>
))}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input value={input} placeholder="Say something..." onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)} autoFocus />
</form>
</div>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Before you start
- Ensure that the Google connection in Auth0 (
google-oauth2) has the following scopes configured:openidprofileemailhttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
import { tool } from "ai";
import { z } from 'zod';
import { google } from "googleapis";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
export const checkUsersCalendar = tool({
description: 'Check user availability on a given date time on their calendar',
parameters: z.object({
date: z.coerce.date(),
}),
execute: async ({ date }) => {
const { token } = await auth0.getAccessTokenForConnection({ connection: 'google-oauth2' });
// Google SDK
const calendar = google.calendar("v3");
const auth = new google.auth.OAuth2();
auth.setCredentials({ access_token: token });
const response = await calendar.freebusy.query({
auth,
requestBody: {
timeMin: formatISO(date),
timeMax: addHours(date, 1).toISOString(),
timeZone: "UTC",
items: [{ id: "primary" }],
},
});
return {
available: response.data?.calendars?.primary?.busy?.length === 0,
};
}
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation.
3. Set up the API route for the chat
import { z } from 'zod';
import { streamText } from "ai"
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai"
import { google } from "googleapis";
import { checkUsersCalendar } from "@/lib/tools/checkUsersCalendar";
export const maxDuration = 60;
export async function POST(req) {
const { messages } = await req.json()
const response = streamText({
model: openai('gpt-4o'),
messages,
system: "You're a helpful AI assistant that can read events from Google Calendar",
tools: { checkUsersCalendar }
})
return response.toDataStreamResponse();
}
4. Call from the client side
'use client';
import { useChat } from '@ai-sdk/react';
export default function Chat() {
const { messages, input, handleInputChange, handleSubmit } = useChat();
return (
<div className="flex flex-col w-full max-w-3xl py-24 mx-auto stretch text-gray-100">
{messages.map(message => (
<div key={message.id} className="whitespace-pre-wrap">
{message.role === 'user' ? 'User: ' : 'AI: '}
{message.parts.map((part, i) => {
switch (part.type) {
case 'text':
return <div key={`${message.id}-${i}`}>{part.text}</div>;
case 'tool-invocation':
return (
<pre key={`${message.id}-${i}`}>
{JSON.stringify(part.toolInvocation, null, 2)}
</pre>
);
}
})}
</div>
))}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input onChange={handleInputChange} value={input} placeholder="Say something..." className="fixed bottom-0 w-full max-w-3xl p-2 mb-8 border border-zinc-300 rounded shadow-xl text-black" />
</form>
</div>
);
}
5. Example UI
Navigate tohttps://localhost:3000 to see the chat UI: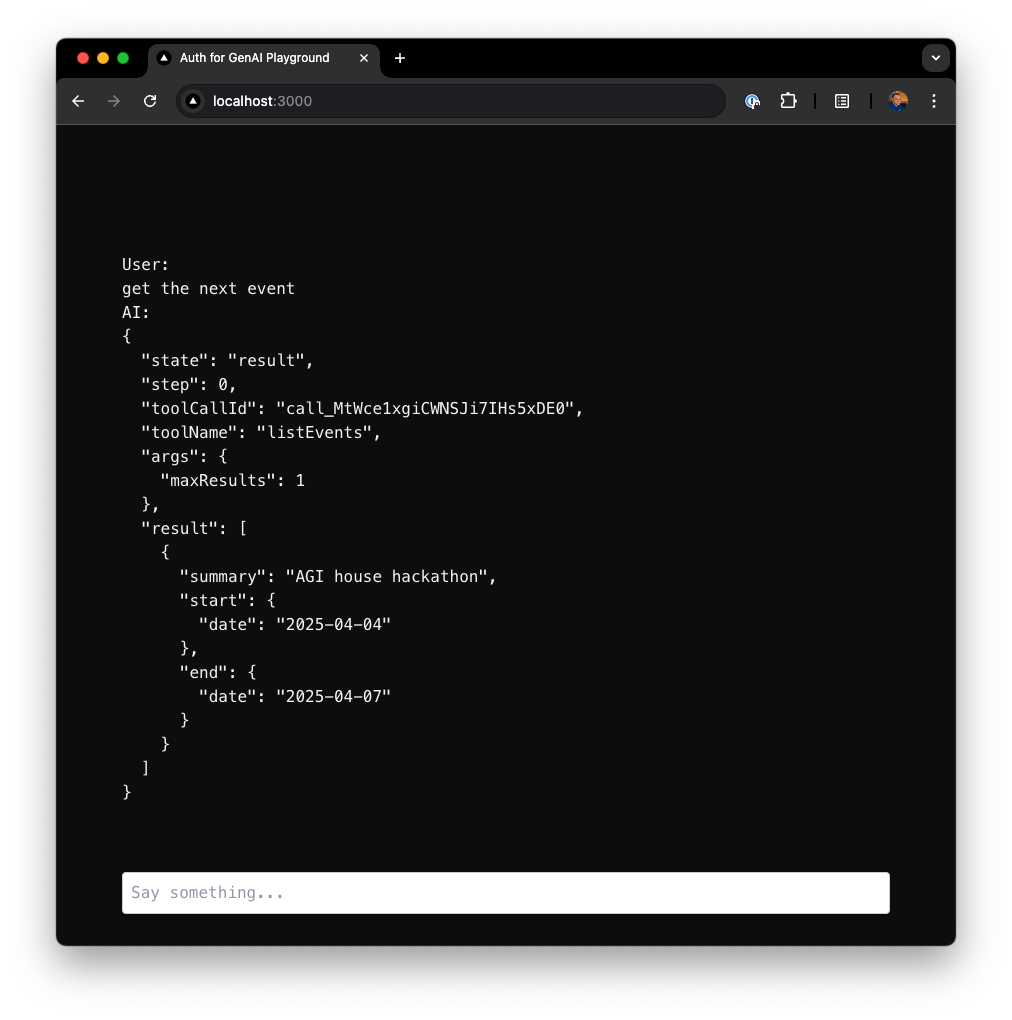 When the user sends a message like
When the user sends a message like Get me the next event, GPT-4 interprets the request and calls the listEvents tool. This tool uses a Google access token (retrieved via Auth0) to fetch upcoming events from the user’s Google Calendar.You can extend the chat UI to display event summaries, highlight meetings, or even visualize the day’s schedule in a timeline view.LangGraph
LlamaIndex
CrewAI
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:pip install auth0-ai-langchain
from auth0_ai_langchain.auth0_ai import Auth0AI
auth0_ai = Auth0AI()
with_google = auth0_ai.with_token_vault(
connection="google-oauth2",
scopes=["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"]
# Optional: By default, the SDK will expect the refresh token from
# the LangChain RunnableConfig (`config.configurable._credentials.refresh_token`)
# If you want to use a different store for refresh token you can set up a getter here
# refresh_token=lambda *_args, **_kwargs:session["user"]["refresh_token"],
)
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from googleapiclient.errors import HttpError
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
from google.oauth2.credentials import Credentials
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain_core.tools import StructuredTool
from auth0_ai_langchain.token_vault import get_access_token_from_token_vault, TokenVaultError
from lib.auth0_ai import with_google
class CheckUserCalendarSchema(BaseModel):
date: datetime
def check_user_calendar_tool_function(date: datetime):
# Get the access token from Auth0 AI
access_token = get_access_token_from_token_vault()
# Google SDK
try:
service = build('calendar', 'v3', credentials=Credentials(token=access_token))
time_min = date.isoformat() + 'Z'
time_max = (date + timedelta(hours=1)).isoformat() + 'Z'
body = {
"timeMin": time_min,
"timeMax": time_max,
"timeZone": "UTC",
"items": [{"id": "primary"}]
}
freebusy_query = service.freebusy().query(body=body).execute()
busy_times = freebusy_query['calendars']['primary'].get('busy', [])
return {"available": len(busy_times) == 0}
except HttpError as e:
if e.resp.status == 401:
raise TokenVaultError("Authorization required to access the Token Vault API")
raise ValueError(f"Invalid response from Google Calendar API: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
check_user_calendar_tool = with_google(StructuredTool(
name="check_user_calendar",
description="Use this function to check if the user is available on a certain date and time",
args_schema=CheckUserCalendarSchema,
func=check_user_calendar_tool_function,
))
ToolNode. The agent will automatically request the access token when the tool is called.from typing import Annotated, Sequence, TypedDict
from langchain.storage import InMemoryStore
from langchain_core.messages import AIMessage, BaseMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
from langgraph.graph import END, START, StateGraph, add_messages
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
from tools.check_availability import check_user_calendar_tool
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[Sequence[BaseMessage], add_messages]
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o")
llm.bind_tools([check_user_calendar_tool])
async def call_llm(state: State):
response = await llm.ainvoke(state["messages"])
return {"messages": [response]}
def route_after_llm(state: State):
messages = state["messages"]
last_message = messages[-1] if messages else None
if isinstance(last_message, AIMessage) and last_message.tool_calls:
return "tools"
return END
workflow = (
StateGraph(State)
.add_node("call_llm", call_llm)
.add_node(
"tools",
ToolNode(
[
# a tool with Token Vault access
check_user_calendar_tool,
# ... other tools
],
# The error handler should be disabled to
# allow interruptions to be triggered from within tools.
handle_tool_errors=False
)
)
.add_edge(START, "call_llm")
.add_edge("tools", "call_llm")
.add_conditional_edges("call_llm", route_after_llm, [END, "tools"])
)
graph = workflow.compile(checkpointer=MemorySaver(), store=InMemoryStore())
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action —such as authenticating or granting API access— before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages such authentication redirects integrated with the Langchain SDK.Server Side
On the server side of your Next.js application you need to set up a route to handle the Chat API requests. This route will be responsible for forwarding the requests to the LangGraph API. Additionally, you must provide therefreshToken to the Langchain’s RunnableConfig from the authenticated user’s session.import { initApiPassthrough } from "langgraph-nextjs-api-passthrough";
import { auth0 } from "@/lib/auth0";
const getRefreshToken = async () => {
const session = await auth0.getSession();
const refreshToken = session?.tokenSet.refreshToken as string;
return refreshToken;
};
export const { GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, runtime } =
initApiPassthrough({
apiUrl: process.env.LANGGRAPH_API_URL,
apiKey: process.env.LANGSMITH_API_KEY,
runtime: "edge",
baseRoute: "langgraph/",
bodyParameters: async (req, body) => {
if (
req.nextUrl.pathname.endsWith("/runs/stream") &&
req.method === "POST"
) {
return {
...body,
config: {
configurable: {
_credentials: {
refreshToken: await getRefreshToken(),
},
},
},
};
}
return body;
},
});
auth0 is an instance of @auth0/nextjs-auth0 to handle the application auth flows. You can check different authentication options for Next.js with Auth0 at the official documentation.
Client Side
In this example, we utilize theTokenVaultConsentPopup component to show a pop-up that allows the user to authenticate with Google Calendar and grant access with the requested scopes. You’ll first need to install the @auth0/ai-components package:npx @auth0/ai-components add TokenVault
import { useStream } from "@langchain/langgraph-sdk/react";
import { TokenVaultInterrupt } from "@auth0/ai/interrupts";
import { TokenVaultConsentPopup } from "@/components/auth0-ai/TokenVault/popup";
const useFocus = () => {
const htmlElRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null);
const setFocus = () => {
if (!htmlElRef.current) {
return;
}
htmlElRef.current.focus();
};
return [htmlElRef, setFocus] as const;
};
export default function Chat() {
const [threadId, setThreadId] = useQueryState("threadId");
const [input, setInput] = useState("");
const thread = useStream({
apiUrl: `${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_URL}/api/langgraph`,
assistantId: "agent",
threadId,
onThreadId: setThreadId,
onError: (err) => {
console.dir(err);
},
});
const [inputRef, setInputFocus] = useFocus();
useEffect(() => {
if (thread.isLoading) {
return;
}
setInputFocus();
}, [thread.isLoading, setInputFocus]);
const handleSubmit: FormEventHandler<HTMLFormElement> = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
thread.submit(
{ messages: [{ type: "human", content: input }] },
{
optimisticValues: (prev) => ({
messages: [
...((prev?.messages as []) ?? []),
{ type: "human", content: input, id: "temp" },
],
}),
}
);
setInput("");
};
return (
<div>
{thread.messages.filter((m) => m.content && ["human", "ai"].includes(m.type)).map((message) => (
<div key={message.id}>
{message.type === "human" ? "User: " : "AI: "}
{message.content as string}
</div>
))}
{thread.interrupt && TokenVaultInterrupt.isInterrupt(thread.interrupt.value) ? (
<div key={thread.interrupt.ns?.join("")}>
<TokenVaultConsentPopup
interrupt={thread.interrupt.value}
onFinish={() => thread.submit(null)}
connectWidget={{
title: "List GitHub respositories",
description:"description ...",
action: { label: "Check" },
}}
/>
</div>
) : null}
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input ref={inputRef} value={input} placeholder="Say something..." readOnly={thread.isLoading} disabled={thread.isLoading} onChange={(e) => setInput(e.target.value)} />
</form>
</div>
);
}
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure you have completed the following steps:Complete the User authentication quickstart to create an application integrated with Auth0.
Set up and configure a Google Cloud project
- Enable the Google Calendar API.
- Create OAuth 2.0 credentials (Web Application) with proper redirect URIs.
Configure a Social Connection for Google in Auth0
- Under the Purpose section, make sure to enable the
Use for Connected Accounts with Token Vaulttoggle. - Under the Permissions section, enable the
Offline Accessscope.
1. Configure Auth0 AI
First, you must install the SDK:pip install auth0-ai-llamaindex
from auth0_ai_llamaindex.auth0_ai import Auth0AI
from flask import session
auth0_ai = Auth0AI()
with_google = auth0_ai.with_token_vault(
connection="google-oauth2",
scopes=["https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.freebusy"],
refresh_token=lambda *_args, **_kwargs:session["user"]["refresh_token"],
)
2. Integrate your tool with Google Calendar
Wrap your tool using the Auth0 AI SDK to obtain an access token for the Google Calendar API.from datetime import timedelta
from googleapiclient.errors import HttpError
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
from google.oauth2.credentials import Credentials
from typing import Annotated
from llama_index.core.tools import FunctionTool
from auth0_ai_llamaindex.token_vault import get_access_token_from_token_vault, TokenVaultError
from src.lib.auth0_ai import with_google
def check_user_calendar_tool_function(
date: Annotated[str, "Date and time in ISO 8601 format."]
):
# Get the access token from Auth0 AI
access_token = get_access_token_from_token_vault()
# Google SDK
try:
service = build('calendar', 'v3', credentials=Credentials(token=access_token))
time_min = date.isoformat() + 'Z'
time_max = (date + timedelta(hours=1)).isoformat() + 'Z'
body = {
"timeMin": time_min,
"timeMax": time_max,
"timeZone": "UTC",
"items": [{"id": "primary"}]
}
freebusy_query = service.freebusy().query(body=body).execute()
busy_times = freebusy_query['calendars']['primary'].get('busy', [])
return {"available": len(busy_times) == 0}
except HttpError as e:
if e.resp.status == 401:
raise TokenVaultError("Authorization required to access the Token Vault API")
raise ValueError(f"Invalid response from Google Calendar API: {response.status_code} - {response.text}")
check_user_calendar_tool = with_google(FunctionTool.from_defaults(
name="check_user_calendar",
description="Use this function to check if the user is available on a certain date and time",
fn=check_user_calendar_tool_function,
))
from datetime import datetime
from llama_index.agent.openai import OpenAIAgent
from src.lib.tools.check_availability import check_user_calendar_tool
system_prompt = f"""You are an assistant designed to answer random user's questions.
**Additional Guidelines**:
- Today’s date for reference: {datetime.now().isoformat()}
"""
agent = OpenAIAgent.from_tools(
tools=[
# a tool with Token Vault access
check_user_calendar_tool
# ... other tools
],
model="gpt-4o",
system_prompt=system_prompt
verbose=True,
)
3. Handle authentication redirects
Interrupts are a way for the system to pause execution and prompt the user to take an action —such as authenticating or granting API access— before resuming the interaction. This ensures that any required access is granted dynamically and securely during the chat experience. In this context, Auth0-AI SDK manages such authentication redirects integrated with the LLamaIndex SDK.Server side
On the server side of your Flask application you will need to set up a route to handle the Chat API requests. This route will be responsible for forwarding the requests to the OpenAI API utilizing LlamaIndex’s SDK, that has been initialized with Auth0 AI’s protection enhancements for tools.WhenTokenVaultInterrupt error occurs, the server side will signal the front-end about the level access restrictions, and the front-end should prompt the user to trigger a new authorization (or login) request with the necessary permissions.from dotenv import load_dotenv
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, session
from auth0_ai_llamaindex.auth0_ai import Auth0AI
from auth0_ai_llamaindex.token_vault import TokenVaultInterrupt
from src.lib.agent import agent
load_dotenv()
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/chat", methods=["POST"])
async def chat():
if "user" not in session:
return jsonify({"error": "unauthorized"}), 401
try:
message = request.json.get("message")
response = agent.achat(message)
return jsonify({"response": str(response)})
except TokenVaultInterrupt as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e.to_json())}), 403
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({"error": str(e)}), 500
Account Linking
If you’re integrating with Google, but users in your app or agent can sign in using other methods (e.g., a username and password or another social provider), you’ll need to link these identities into a single user account. Auth0 refers to this process as Account Linking. Account Linking logic and handling will vary depending on your app or agent. You can find an example of how to implement it in a Next.js chatbot app here. If you have questions or are looking for best practices, join our Discord and ask in the#auth0-for-gen-ai channel.
